[jg-ffw]

[/jg-ffw]
What is Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is a genetic condition that typically causes some level of learning disability and certain physical characteristics. Some children with Down syndrome have additional health problems such as heart defects with varying severity. With specialist care and education, some children with Down syndrome can integrate into mainstream schools and lead semi-independent lives.
Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21 in a baby’s cells. It occurs by chance at conception and there is no evidence that anything done before or during pregnancy causes the syndrome. About 1 in 700 pregnancies will have the chance to carry a baby with Down syndrome and the probability increases with the pregnant woman’s age. Antenatal screening for Down syndrome can help identify the condition before birth.
Types of Down Syndrome
There are three causes of Down syndrome:
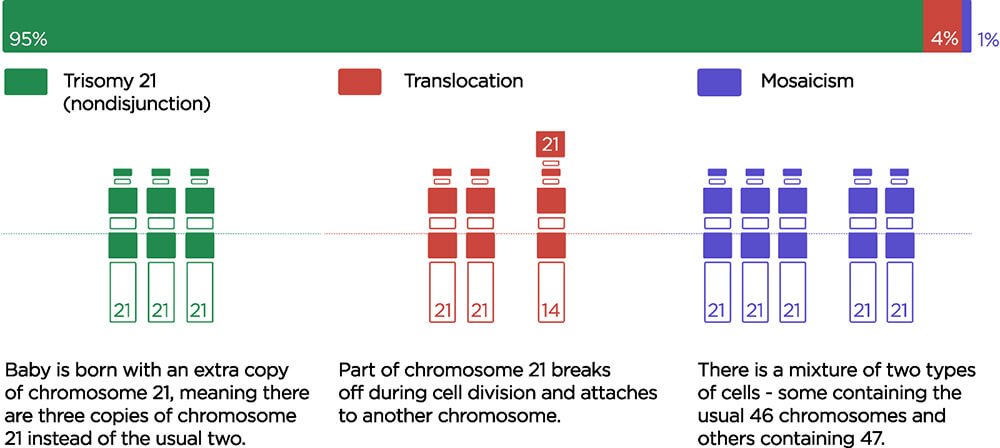
Trisomy 21
An estimated 95 percent of people with Down syndrome have trisomy 21, meaning they have three number 21 chromosomes instead of two. We normally have 23 pairs of chromosomes, each made up of genes.
Translocation
In translocation, which accounts for about 4% of cases of Down syndrome, the total number of chromosomes in the cells remains 46. However, an additional full or partial copy of chromosome 21 attaches to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14. The presence of the extra full or partial chromosome 21 causes the characteristics of Down syndrome.
Mosaicism
In mosaicism, the person with Down syndrome has an extra 21st chromosome in some of the cells but not all of them. The other cells have the usual pair of 21st chromosomes. About 1 to 2 percent of people with Down syndrome have this type.